HEALPix Facility Installation Guidelines
This document describes the installation for the HEALPix facilities.
Eric Hivon, Anthony J. Banday, Matthias Bartelmann, Benjamin D. Wandelt,
Frode K. Hansen and Krzysztof M. Górski
Revision: Version 3.83; November 13, 2024
https://healpix.sourceforge.io
http://healpix.sf.net
In this document the installation procedure for the HEALPix
distribution is outlined. HEALPix comprises a suite of Fortran 90, C++,
IDL, Java and Python routines
providing both stand-alone facilities and callable subroutines as an alternative
for those users who wish to build their own tools.
A set of C subroutines and functions is also provided.
The distribution can be downloaded as a gzipped tarred file, or as a zipped file,
which can respectively be unpacked by executing the commands1
% gunzip Healpix_3.83.tar.gz
% tar -xpf Healpix_3.83.tar
or
% tar -xzpf Healpix_3.83.tar.gz
or
% unzip Healpix_3.83.zip
creating a directory named Healpix_3.83 whose structure is shown in Figure
1.
Figure 1:
The directory structure for the HEALPix distribution.
|
|
As with most freely available software, the distribution
comes with caveats, the major one being that although we have attempted
to automate the installation as much as possible, not all eventualities
can ever be foreseen. We have tested the installation on the following
platforms:
AIX, IRIX, IRIX64, Linux, SunOS, ALPHA and Darwin (MacOS)
There may be problems in the facility build due to the local system
configuration which is beyond our control.
Installation Requirements
Table 1:
Documentation on the installation and usage of the different packages
|
|
The major part of the HEALPix distribution is written in both Fortran 90 and C++ and
so the appropriate compiler(s) must be present (Linux and Darwin users should look
at Section 7.1 about free F90 compilers. Microsoft Windows
users should look at Section 7.2). Many visualisation tools and map
manipulation routines are provided in IDL (please note
that at least version 6.4 is required), Java and Python. Some of the HEALPix routines are
also available in C.
Starting with version 3.0, the
healpy
(HEALPix in Python) library has been integrated into HEALPix releases. Since it
is, to a large extent, a
wrapper to the C++ routines, installing it also requires a C++ compiler (on top
of python and a few supporting Python libraries) but it will perform
its own compilation of the current HEALPix C++ library.
Starting with version 3.10, all the (computation intensive) Spherical Harmonics
operations required by the C++, Fortran and Python routines
are performed with the highly optimized C-written libsharp library,
also included in the package, and which was further optimized in
version 3.60.
This section and the next focus on the compilation and installation of the
C, C++, Fortran 90, IDL and
Python routines and libsharp library. For more information on the
Java routines see table 1.
The configure script is written in the Bourne shell. The script
attempts to generate a Makefile which is tailored to one of
the above Operating Systems (OS's) and using
Makefile.in as a template for non system-specific statements.
Only the basic UNIX make facility is required to build the software, although we do
still recommend the GNU make facility (https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/make/).
In addition, several environment configuration files and an IDL/GDL/FL startup file are
generated. These automatically establish
various environment variables and aliases to make the use of the
HEALPix package simpler.
The HEALPix Fortran 90, C++, C and Python distributions also
require the publicly available CFITSIO library.
Versions 4.2.0 (Nov 2022) or higher are recommended since they simultaneously meet
Fortran 90 routines requirements, fix previous security vulnerabilities
and are compatible with Apple's ARM chips.
The IDL visualization software is commercially
available at
while the GNU Data Language GDL, a free open clone of IDL 7.1,
or
the freeware Fawlty Language FL, a free closed clone of IDL 8,
can also be used (with some
caveats, listed respectively in §7.9 and §7.10) and can be downloaded for free from
As it was already the case in version 1.20, users no longer need to acquire the
IDL
Astronomy User's Library
(https://github.com/wlandsman/IDLAstro)
or the COBE (IDL) Analysis Software (https://lambda.gsfc.nasa.gov/product/cobe/cgis.cfm),
although we do recommend these packages to the user.
The 100-odd routines required for version 3.83 are contained in the
subdirectory Healpix_3.83/src/idl/zzz_external.
These procedures are included in the HEALPix package unchanged and
solely for the purpose of making it self contained. In this way,
we remove the burden of installation of additional libraries from
the end user.
The Python healpy package requires
While not required, the
IPython (https://ipython.org)
and
jupyter (https://jupyter.org)
interfaces can also be useful.
A parallel implementation (based on OpenMP, for shared memory architectures) of the Spherical Harmonics
Transforms involved in F90 synfast, anafast, smoothing, plmgen, alteralm
and C++
synalm_cxx, alm2map_cxx, anafast_cxx, smoothing_cxx, rotalm_cxx ... is now
available by default and can be readily compiled and used with the standard installation script.
A set of routines with MPI parallelization (for distributed memory architectures)
is also available for Spherical Harmonics Transform, thanks to the work of H.K. Eriksen
(UIO) and Snorre Boasson (ITEA, NTNU). See the F90
subroutines documentation for more information on how to use those routines in
your code.
We found that it was remarkably difficult to find
random number generators in the public
domain which are simple yet
powerful and easy to use.
We are providing one (both in C++ and F90) which is an adaptation of an xorshift generator described
in Marsaglia (Journal of Statistical Software 2003, vol 8). It has a theoretical period of
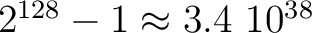 .
.
healpix_doc: an easy access to HEALPix documentation
The shell script healpix_doc now is available to provide easy
access to the HTML, PDF and/or EPUB documentation of all Healpix packages.
It will automatically open a web browser, a PDF viewer, or an EPUB viewer (among those found on the
system) on the documentation
available locally (at $HEALPIX/doc) or on remote web sites. To use it, simply type
$HEALPIX/healpix_doc -e or
$HEALPIX/healpix_doc -h or
$HEALPIX/healpix_doc -p
to access respectively the EPUB, HTML and PDF documentation. The default browser and
viewers used by healpix_doc can optionally be set with the
environment variables
$HEALPIX_HTML_BROWSER,
$HEALPIX_EPUB_VIEWER and
$HEALPIX_PDF_VIEWER.
EPUB
is an open e-book format whose dynamical layout allows the same document to be read comfortably on
screens of any size.
It is supported by many commercial and free e-readers, with sometimes unequal results.
Among the free ones we tested, we can recommend
- ebook-viewer, included in the open source Calibre e-book manager package
(https://calibre-ebook.com, used to generate the HEALPix EPUB files)
available for many platforms, including Linux, MacOS and Windows,
- Books (formerly iBooks), pre-installed in MacOS and available for download
for iOS and watchOS,
- the cost-free, ad-free
Lithium EPUB reader
for Android.
If the user has one of the supported OS's, then installation proceeds utilizing
the following commands. If your OS is not supported, the configuration step
should be omitted, Makefile.in should be copied as Makefile and explicitly
tailored to the user environment.
| % ./configure [-L] [—auto=<list>] |
uses Makefile.in as a template to build
the correct Makefile (from user inputs as required), it
will also configure the IDL/GDL/FL routines |
| % make |
builds all the facilities |
| % make test |
tests all the facility previously compiled |
| % make clean |
removes object (*.o) files |
| % make tidy |
removes object files, module files (*.mod), executables and libraries |
| % make distclean |
same as above and restores the directories to the state of the
original distribution |
These different steps are detailed below.
./configure [-L] [—auto=<list>] [-h] [-v]
The ./configure script manages the configuration of the C, C++,
Fortran90, IDL and Python suites of routines and facilities.
An online help is available with
./configure -h, while
./configure -v
will return the HEALPix release number (currently 3.83) and exit.
The -L option can be used to write the HEALPix specific configuration files
into the HEALPix directory itself rather than in installer's home directory (see
§4.1.1).
Using the -L option is recommended when doing a project or system wide installation of
HEALPix to be accessed by several different users.
Two new features have been introduced in version 3.60.
- The configure script now supports the -–auto=<list>
option to perform an automated (batch) configuration of the various packages using default answers
provided by the script (possibly customized with environment variables described below)
where <list> is a comma separated list of items to be configured, to be chosen (and combined)
among
- all: (re-)configures everything;
-–auto=all is the same as -–auto=profile,sharp,c,cxx,f90,idl,healpy;
- c: configures C and the required items, same as profile,c;
- cxx: configures C++ and the required items, same as profile,cxx,
libsharp will also be configured, compiled and installed if it was not previously done;
- cpp: same as cxx (see above);
- f90: configures F90 and the required items, same as profile,f90,
libsharp will also be configured, compiled and installed if it was not previously done;
- idl: configures IDL and the required items, same as profile,idl;
- sharp: forces the (re-)configuration, compilation and installation of libsharp (required by F90 and C++);
- profile: configures user or system configuration files (required by C, C++, F90 and IDL);
- healpy: configures healpy.
- If the environment variables
CC (C compiler, relevant for C,C++,F90,healpy,sharp),
C_FITS, C_SHARED (C),
CXX, CXXFLAGS, CXX_PARAL (C++),
FC, F_AR, F_DIRSUFF, F_OPT,
F_PARAL, F_SHARED (F90),
FITSDIR, FITSINC (C,C++,F90),
PYTHON (healpy),
PROFILE_EDIT (profile),
SHARP_COPT, SHARP_PARAL (sharp),
and papersize, ps_com, pdf_com, gif_com (IDL)
are defined prior to calling the configure script, they will change the
default values proposed in the (interactive or automated) configuration process.
The online help ./configure -h will show the current value of these variables.
As detailed further down, several of these variables are boolean in nature, with the values
1, y, Y, t or T meaning 'true',
and
0, n, N, f or F meaning 'false'.
These two new features can of course be combined.
For instance, in Bourne related shells (eg, sh, bash, dash, ksh, zsh), the command
FC=ifort CC=icc ./configure -–auto=f90
and in C related shells (eg, csh, tcsh)
setenv FC ifort ; setenv CC icc ; ./configure -–auto=f90
will automatically run the configure script for the libsharp (if not previously done)
and f90 package items, using Intel's Fortran and C compilers.
Configuration profile
A feature introduced in previous releases and enhanced since v2.10, is that
the configure script creates a shell configuration file
(located in
${HOME}/.healpix/3_83 _ OS_TYPE
OS_TYPE /config
or in
/config
or in
${HEALPIX}/confdir/3_83 _ OS_TYPE
OS_TYPE /config
if ./configure -L was used)
according to shell
type in which various environment variables and aliases are defined
for your convenience. If you agree upon prompting
(or set the boolean
environment variable PROFILE_EDIT to an affirmative value),
it will also change your default system profile during installation to
automatically source this profile. If you do not agree to this change
(or set the boolean environment variable PROFILE_EDIT to a false value),
you will need to explicitly source the configuration file above for any session in
which you intend to run HEALPix facilities.
In particular, you will have to make sure that the HEALPIX system variable is correctly
defined (as the full path to the HEALPix directory) before running
the package.
/config
if ./configure -L was used)
according to shell
type in which various environment variables and aliases are defined
for your convenience. If you agree upon prompting
(or set the boolean
environment variable PROFILE_EDIT to an affirmative value),
it will also change your default system profile during installation to
automatically source this profile. If you do not agree to this change
(or set the boolean environment variable PROFILE_EDIT to a false value),
you will need to explicitly source the configuration file above for any session in
which you intend to run HEALPix facilities.
In particular, you will have to make sure that the HEALPIX system variable is correctly
defined (as the full path to the HEALPix directory) before running
the package.
The ./configure script will ask for the C compiler and options to
be used, and for the full path of an installed cfitsio library to (optionally) link to.
By default, only a static library is created, but the user can also ask for
a shared (Unix/Linux systems) or dynamic (Darwin) library.
The environment variables CC, C_FITS (boolean), FITSDIR, FITSINC
and C_SHARED (boolean) can be used to control the script behavior.
After compilation
(see make section) and linking, all libraries will be
in ${HEALPIX}/lib/chealpix.* .
See also §6 on pkg-config.
C++ configuration
Starting with version 3.60, the ./configure script will be used to
provide information (like the choice of C++ compiler and options)
to an automated (autoconf generated) configure script,
(located in src/cxx/configure), which will take care of the configuration.
The environment variables CC, CXX, CXXFLAGS, FITSDIR and FITSINC
can be used to customize the whole process. If the latter two are not explicitely set,
the autoconf configure script will look for a cfitsio installation on its own.
The configuration of libsharp will be also taken care of at this stage.
The boolean variable CXX_PARAL, introduced in version 3.80 and defaulting to 1 (=true), controls whether the code will be parallelized (with OpenMP) or not. To obtain a serial implementation of the code, set CXX_PARAL=0 and make sure no OpenMP related flags appear in CXXFLAGS.
At odds with previous versions, the C++ binaries, libraries and header files will be installed in
${HEALPIX}/bin,
${HEALPIX}/lib and
${HEALPIX}/include directories respectively.
If the HEALPix configuration file is sourced as described in §4.1.1, the full path to the C++
executables will be added to the environment PATH variable.
See also §6 on pkg-config.
When you run ./configure on a supported system
you will be prompted to enter compiler optimisation flags.
We have not attempted to provide the best optimisation flags for all
operating systems. The configure
script will have a guess at optimisation options for some systems, but it
is up to the user to figure out an optimal set2.
From our experience,
we have not found significant accumulation of numerical error even
when using the most aggressive optimisation level available.
The environment variable FITSDIR, CC, FC,
F_AR, F_DIRSUFF, F_OPT,
F_SHARED (boolean) and F_PARAL (boolean) can be used to customize the configuration.
The configuration of libsharp will be also taken care of at this stage.
If the HEALPix configuration file is sourced as described in §4.1.1, the full path to the F90
executables will be added to the environment PATH variable.
See also §6 on pkg-config.
IDL/GDL/FL configuration
You will be asked for the external applications, such as gv, xpdf, display,
 you want to use to visualize the
GIF, JPEG, PDF, Postscript and PNG files created by IDL, GDL or FL.
you want to use to visualize the
GIF, JPEG, PDF, Postscript and PNG files created by IDL, GDL or FL.
The environment variables papersize, ps_com, pdf_com and gif_com can be
used to customize this configuration.
If the HEALPix configuration file is
sourced as described in §4.1.1, the aliases
hidl (hidlde),
hgdl (hgdlde) and/or
hfl (hflde)
are also defined to give you access to HEALPix routines from respectively IDL, GDL and/or FL,
with a command-line (or graphical) interface.
See the HEALPix IDL Document
for more
information on using HEALPix IDL/GDL/FL together with other IDL libraries, and §7.9,7.10 on using GDL or FL instead of IDL.
Java installation
The configuration and installation of the HEALPix Java package is currently
handled separately. See table 1 for more information.
Python (healpy) installation
Starting with version HEALPix-3.83 (healpy-1.18) python wheels
will be generated by the package installer pip3 (https://pypi.org/project/pip), instead of .egg files previously generated by
easy_install.
The ./configure script will ask for the Python command you want to use
(in case several coexist on your computer) and check that its version number
meets the healpy requirements (see above), as well as for C and C++
compilers,
and finally the list of arguments you want to pass to the pip command. The latter default value is
“install . -–user”, where the dot (.) refers to
the local healpy source directory (${HEALPIX}/src/healpy). The -–user flag can be dropped if
the installation is made system-wide (by a root user) or in a virtual
environnement (like for instance in conda),
while the flag -e or -–editable can be inserted (ie, looking
like 'install -e . -–user') to keep the installed package editable.
The environment variables PYTHON, C, CXX and
PIPARGS can be used to customize the configuration process.
Note that during the compilation with make (see below), the
pip command will prompt a fresh compilation of the
${HEALPIX}/src/cxx/* libraries, with all the options necessary to Python linkage, and
can be done independently of the C++ installation described above.
Note also that the healpy compilation will very likely
require an active network connection in order
to download on the fly some of the required Python ancillary packages.
libsharp library
The libsharp C-written library for optimized Spherical Harmonics operations
is used by the C++, Fortran, IDL and healpy routines and facilities.
Starting with version 3.60, a new, faster, implementation is in use,
and will be configured (only once) at the same time as any of the C++ or Fortran packages,
but can also be configured on its own.
The environment variables CC and SHARP_COPT can be used to set respectively
the C compiler and its options proposed during the interactive or automated configuration process.
For optimal performance, the C compilation flags should include -ffast-math
and -march=native (or your compiler's equivalent options), and may look like
SHARP_COPT='-O3 -ffast-math -march=native -fopenmp' (multi-worded values must be enclosed in quotes).
If you are using gcc or clang (see below) and you want to produce a portable,
high-performance library, and if you compiler and assembler support it,
you can also replace -march=native by -DMULTIARCH.
If you are using clang to compile libsharp,
make sure it supports OpenMP (as in version 3.7 or more), and that OpenMP
is enabled explicitly among the compiler options
(possibly requiring the flag -fopemp=libomp or -fopemp=libiomp5
instead of the usual -fopemp
or by specifying the location of the OpenMP libraries during compilation and at run time).
The boolean variable SHARP_PARAL, introduced in version 3.80 and defaulting to 1 (=true), controls whether the library will be parallelized (with OpenMP) or not. To obtain a serial implementation of libsharp, set SHARP_PARAL=0 and make sure no OpenMP related flags appear in SHARP_COPT.
After compilation and installation (which, for libsharp only,
are done as early as the configure step)
the resulting library will be in
${HEALPIX}/lib/libsharp* and the header files in
${HEALPIX}/include/libsharp/sharp*.h.
See also §6 on pkg-config.
The
make
command will compile one or several of the C, C++, F90, libsharp and Python packages
depending on what was configured with the ./configure script.
Specific packages can be compiled with the respective commands
make c-all
make cpp-all
make f90-all
make sharp-all
make healpy-all
To perform several compilation jobs simultaneously, the command make -j [number_of_jobs]
can be used.
Please neglect any possible warnings at compile time. If you run into
trouble please refer to the section Troubleshooting and further
information.
After running make, the user must re-login to ensure that the new profiles built by the installation
procedure are correctly sourced. Only then will the
user have full access to the specific HEALPix
environment variables etc.
All installed libraries and executables can be tested with
make test
while specific tests of the C, C++ and Fortran products can be performed with,
respectively
make c-test
make cpp-test
make f90-test
make sharp-test
make healpy-test
For f90-test, Table 2 lists the codes tested with the
parameter files used, as well as the data files produced and the respective
reference files.
Notes:
In order to test the new HEALPix profile set-up one can then attempt
to run any C++ or F90 facility from any directory on your system. Similarly,
IDL, GDL or FL can be tested by invoking respectively
hidl (or hidlde), hgdl (or hgdlde), or hfl (or hflde).
Three levels of cleaning are available:
make clean
will remove the intermediate files created during compilation, such as object
files, (Fortran) modules files, ... found in the source or build directories;
make tidy
same as above, and will also remove the HEALPix executables, libraries and module and/or
include files;
make distclean
will return the HEALPix directory to its original 'distribution' state by discarding the same
files as above, as well as the executable and library directories and the top
level Makefile.
As a consequence, make clean can be used after a successful compilation and installation in order to remove now useless intermediate files while keeping the codes functional,
while
make tidy should be used between consecutive (failed) attempts with different compilers, compiler versions or compiler options, to avoid any conflict between new and pre-existing files.
Third party or user-developed codes may require HEALPix as an external library.
An easy way to achieve this linking is to use the pkg-config facility
(now available on many systems, including Linux, Unix*, MacOS and MS Windows),
following the procedure described in §6 on pkg-config.
As a result of the line added to your shell profile which explicitly
sources the HEALPix profile, care must be taken if the package
is reinstalled in a different directory. If such reinstallation
is desired, the included line must be removed from your system profile,
allowing the corrected version to be added.
Pkg-config files
Starting with HEALPix 3.12, pkg-config (.pc) files are generated
during the configuration of the
libsharp,
C,
C++ and
F90 packages, and are initially located respectively in
${HEALPIX}/lib/pkgconfig/libsharp.pc,
${HEALPIX}/lib/pkgconfig/chealpix.pc,
${HEALPIX}/lib/pkgconfig/healpix_cxx.pc,
and
${HEALPIX}/libsuffix/pkgconfig/healpix.pc.
If the
pkg-config software
is available on your system (see
https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/pkg-config/ to download, install and
use it) and if the location of
the HEALPix pkg-config files above are known to it (either by moving/copying them
to one of the standard locations returned by
pkg-config -–variable=pc_path pkg-config
or by customizing the environment variable PKG_CONFIG_PATH4),
then linking your own or third-party code with the
C,
C++,
F90 HEALPix library simply becomes
cc `pkg-config -–cflags -–libs chealpix` mycode.c -o mycode
c++ `pkg-config -–cflags -–libs healpix_cxx` mycode.cpp -o mycode
FC `pkg-config -–cflags -–libs healpix` mycode.f90 -o mycode
(where FC has to be replaced by the Fortran compiler used to generate the
HEALPix library).
Troubleshooting and further information
This section contains a list of difficulties which we have dealt
with. It is by no means exhaustive.
In case of problems, see https://healpix.sourceforge.io/support.php or contact healpix-support at lists.sourceforge.net
Free Fortran90/95 Compilers
Some free Fortran90/95 compilers that can be used to compile HEALPix are listed below.
They all support the few Fortran 2003 features used in HEALPix.
- Intel Fortran compilers for Linux based computers ifx
(since version 2021) and previously
ifort (versions
11.* to 19.*5)
https://software.intel.com/en-us/fortran-compilers
- GNU Fortran 95 compiler (gfortran) included in GNU Compiler Collection GCC version 4.0.0
and up and available for Linux, Mac OSX, Windows, Sun ... platforms
https://www.gnu.org/software/gcc/fortran/.
GFortran binaries for all platforms can also be downloaded from
https://gcc.gnu.org/wiki/GFortranBinaries.
Please note that only recent versions of gfortran (Aug 2005
and later) compile HEALPix correctly, and v4.2.1 and more have given satisfying
results so far, including native OpenMP support.
- Nvidia's LLVM-based Fortran compiler (flang) available as pre-compiled executables and libraries for Linux
https://www.scivision.co/flang-compiler-build-tips
and as source files for all platforms
https://github.com/flang-compiler/flang/wiki/Building-Flang.
- Nvidia's PGI Fortran (formerly Portland Group) compilers (pgf90) available as freemium (without support) or commercially for Linux, Mac OSX and Windows from
https://www.pgroup.com/index.htm.
- G95 compiler available for Linux, Mac OSX, Windows, Sun and HP platforms with 32 and 64 bit architectures (eg, x86 and x86-64). In the latter case, the '32bit default integer' (32bit DI) version of g95 must be used. Note that this compiler was last released in 2013, and it generally generates slower codes
than the compilers listed above.
http://www.g95.org
See http://fortranwiki.org/fortran/show/Compilers for an extended list of free, freemium and commercial Fortran compilers.
Installation under Microsoft Windows
Detailed instructions to install HEALPix on Windows 7 using Cygwin, kindly provided by John Arballo,
are available in §7.2.1,
while other configurations are discussed in §7.2.2.
Installation on Windows 7 with Cygwin
The three steps (installation of Cygwin, cfitsio and HEALPix respectively) must be done in that order.
A: Install Cygwin
- Go to https://www.cygwin.com/and click on `Install Cygwin' in the menu on the left.
- Click on setup-x86.exe (for 32-bit installation) or
setup-x86_64.exe
(for 64-bit installation) and then `Save File' when prompted.
- Go to your Downloads folder (or wherever you saved setup-x86*.exe) and
double-click on the setup-x86*.exe file to run it.
- Accept all defaults, except:
- You have to `Choose A Download Site'. (eg:
https://ftp.gtlib.gatech.edu).
- When prompted to `Select Packages', expand `Default' (if you see a `+'
to the left of it), expand `Devel', then find and add the following
packages (click on `Skip' for each of them so it changes to the
version number and a checkbox appears in the `Bin' column):
gcc-core
gcc-fortran
gcc-g++
make
The installation will take a few minutes.
B: Install CFITSIO Library
- Get the latest source code package from NASA's HEASARC website
(https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/FTP/software/fitsio/c/cfitsio_latest.tar.gz).
When prompted to save the file, in the Save dialog window, navigate to
C:\cygwin64\usr\local
(assuming you accepted the defaults when installing Cygwin), click on
`New folder' and name it `src', go into that folder and `Save'.
- Open a Cygwin terminal (via the new Desktop icon or through your Start
menu).
- Enter the following commands at the '$' prompt:
$ cd /usr/local/src
$ tar zxvf cfitsio_latest.tar.gz
$ cd cfitsio
$ ./configure -–prefix=/usr
$ make
$ make install
$ cd ../
- Leave the Cygwin terminal open.
C: Install HEALPix
- Get the latest version of HEALPix from SourceForge
(https://sourceforge.net/projects/healpix/files/latest/download). When
prompted to save the file, save it in
C:\cygwin64\usr\local\src.
- In Windows Explorer, navigate to
C:\cygwin64\usr\local\src,
right-click on Healpix_3.83_*.zip and `Extract all...'. Accept the
default location.
- In the Cygwin terminal, type the following commands at the
'$' prompt
(use the names of the Healpix directories for
the version you installed):
$ cd Healpix_3.83_*
$ cd Healpix_3.83
$ ./configure
Select an option from the menu (e.g., `2' for the C
package) and accept all of the defaults except that
the first time
you run configure, you'll be prompted at the end to modify your
home shell profile ('.profile'). Enter `y' at this prompt.
$ make
$ make test
$ make tidy
Other Windows configurations
Installation on Windows versions other than 7 should be very similar to the one detailed above.
In step A above, replacing Cygwin with MinGW (http://www.mingw.org/)
together with the MSYS collection of GNU utilities
(see http://www.mingw.org/wiki/msys and
https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw/files) is also possible.
The Unix/Linux tools required include sh, make, awk, grep, sed, ls, wc, cat, more, nm, ar,
as well as C, C++ and Fortran compilers.
The latest gfortran binaries for Cygwin and/or MinGW can be found at, eg
https://cygwin.com/cgi-bin2/package-grep.cgi?grep=gcc-fortran&arch=x86_64,
following the tips found at
https://gcc.gnu.org/wiki/GFortranBinaries.
The most common problem with the Fortran HEALPix compilation will produce
messages like:
ld: Undefined symbols:
_ftbnfm_
_ftclos_
_ftcrhd_
_ftdkey_
...
or
fitstools.f90: undefined reference to `ftdkey_'
fitstools.f90: undefined reference to `ftbnfm_'
fitstools.f90: undefined reference to `ftclos_'
...
or
Undefined symbols:
"_ftghbn_", referenced from:
___fitstools_MOD_read_fits_cut4.clone.2 in libhealpix.a(fitstools.o)
___fitstools_MOD_getsize_fits.clone.1 in libhealpix.a(fitstools.o)
___fitstools_MOD_getsize_fits in libhealpix.a(fitstools.o)
...
ld: symbol(s) not found
collect2: ld returned 1 exit status
and occurs when the CFITSIO installation script could not find a valid fortran compiler.
To solve this problem
- Go into the CFITSIO directory.
Assuming that ifort is available on your
system (it can be replaced below by gfortran, g95, f77, f2c,  ) type:
) type:
./configure FC=ifort
make
make install (optional).
- Then go back into the HEALPix directory and do
./configure (making sure that you are using the newly created libcfitsio.a library)
make
make test
See also the note below on 64 bit architectures.
- Linux, Mac OS X
If the HEALPix codes are compiled in 64 bits, and the GNU C Compiler (gcc) is used to compiled CFITSIO, then issue the following commands in the
CFITSIO directory:
./configure FC='gcc -m64'
make
You can
then force compilation to the same binary format by entering
-m64 when asked for the optimisation options in the
HEALPix configure script.
- IRIX64
On a 64-bit architecture such as IRIX64, CFITSIO will have to be
compiled in the same binary format as the HEALPix codes.
This can be achieved by typing the
following on the
command line in the CFITSIO directory:
rm config.cache
setenv CC 'cc -n32'
./configure
make
Alternatively you can replace the -n32 with -64. You can
then force compilation to the same binary format by entering either
-n32 or -64 when asked for the optimisation options in the
HEALPix configure script.
A particular problem encountered with the CFITSIO Version 2.0 release relates
to the inclusion of various libraries within the system release for a given
machine. This led to some modifications to the Makefile to include the specific
library links -lm -lnsl -lsocket on SunOS, but only -lm for IRIX64.
If your OS is not completely supported by the distribution, you may find this
as one source of errors. The CFITSIO developers recommend compilation of the
testprog routine. Inspection of the libraries linked after executing the
make testprog statement will reveal those you need to include in the
Makefile.
Some problems have been reported on Debian/Linux systems during the
linking to the CFITSIO library shipped with Linux. If these problems
occur, try to recompile the CFITSIO library from scratch before linking
to HEALPix.
CFITSIO and libcurl
Starting with version 3.42, CFITSIO is by default linked with the
curl library (https://curl.haxx.se/libcurl,
used to read remote FITS files via https) whenever it is available.
This shared or dynamic library is pretty standard on modern systems,
and often located in /usr/lib or /usr/lib64, and the command curl-config
can be used to determine its location.
In this case, when executing the HEALPix code,
the system must know where to find this library at runtime as explained for instance
here
for Linux/Unix or
there
for MacOSX.
CFITSIO from Heasoft
The Heasoft suite of software packages for High Energy Astrophysics,
also hosted at HEASARC and available as source files or precompiled binaries,
includes a cfitsio library and its header files.
However, trying to link HEALPix to that installation of cfitsio will generally fail, because
- the precompiled cfitsio library may not be properly detected during the configuration of
HEALPix (in C, C++ and F90),
- the Heasoft header files
rotmatrix.h and
pointing.h found in
${HEADAS}/include (like
fitsio.h) will conflict with the ones provided in
${HEALPIX}/src/cxx/cxxsupport,
preventing the compilation of HEALPix C++ routines.
It is therefore recommended to link HEALPix to a cfitsio library compiled
locally and not included in Heasoft.
If Heasoft's cfitsio is to be used,
Heasoft must have been compiled locally from source files,
and the paths provided during the HEALPix configuration must be
FITSDIR=${HEADAS}/../heacore/PLATFORM/lib and
FITSINC=${HEADAS}/../heacore/PLATFORM/include
(instead of the expected
FITSDIR=${HEADAS}/lib and
FITSINC=${HEADAS}/include)
where PLATFORM depends on your computer and operating system and may look like x86_64-pc-linux-gnu-libc2.29.
If HEALPix-F90 codes (or any other Fortran code) are linked with cfitsio on Apple's
ARM chips (M1 and M2), then version 4.1.0 (March 2022) or above of cfitsio must
be used, see Section 2.
This by itself is no cause for concern. When comparing using a
diff on the test files will most likely report a
difference even when the installation has been successful.
This may be due to the fact that
different installations have different floating point
representations. Also, the FITS files carry date information.
If you have unforeseen problems at runtime, try unlimit (under csh or tcsh) or ulimit (under sh or bash), in order to increase the heap and stack memory size. It
sometimes helps.
We have found that in very rare cases the alias hidl
is not recognised by the user's system. Usually, this is related
to the local system's IDL script. A quick-fix is achieved
by setting the environment variable IDL_STARTUP to be
equal to the HEALPix startup file HEALPix_startup
including the directory path to the file. This enables
the user to access the HEALPix IDL procedures simply by invoking
IDL. For example, in the typical installation documented
above for a user running the tcsh shell, the command
setenv IDL_STARTUP
/disk1/user1/HEALPix_3.83/src/idl/HEALPix_startup
should be issued (or added to the user's shell profile).
If the user already has an IDL startup file, then
this should be merged with HEALPix_startup. This temporary
solution does mean that the HEALPix IDL procedures are available
in the IDL_PATH at all times, which may lead to conflicts with
user-defined procedures. The hidl invocation was intended
to circumvent these issues, allowing HEALPix IDL procedures to
be available only when desired.
A proper fix requires the user to ask the local system
administrator to adjust the local IDL script.
See the homonymous section in the "IDL Facilities Overview"
Mac OS X, X11 and IDL cursor
If the IDL cursor does not work correctly on X11 windows under Mac OS X, and the
2nd and 3rd button clicks are ineffective,
type
- with Apple's X11:
- under Tiger (10.4.*):
defaults write com.apple.x11 wm_click_through -bool true
- under Leopard (10.5.*), Snow Leopard (10.6.*) and Lion (10.7.*):
defaults write org.x.x11 wm_click_through -bool true
- with Xquartz (default under Moutain Lion (10.8.*), Mavericks (10.9.*) and Yosemite (10.10.*),
available for download for
El Capitan (10.11.*), Sierra (10.12.*), High Sierra (10.13.*), Mojave (10.14.*),
Catalina (10.15.*), Big Sur (11.*), Monterey (12.*), Ventura (13.*), Sonoma
(14.*) and Sequoia (15.*)):
defaults write org.macosforge.xquartz.X11 wm_click_through -bool
true for Xquartz 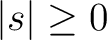 2.7.*, or
2.7.*, or
defaults write org.xquartz.X11 wm_click_through -bool true
for Xquartz  2.8.*
2.8.*
- with MacPort's X11 (package xorg-server):
defaults write org.macports.X11 wm_click_through -bool true
at your X11 prompt and restart X11.
Note that the command ls -lrt $HOME/Library/Preferences/*[xX]11*plist
can be used to determine the X window system installed on
your Mac.
See also http://www.idlcoyote.com/misc_tips/maccursor.html and
mollcursor documentation in "IDL
Facilities").
Using GDL instead of IDL
GNU Data Language (GDL), is a free clone of IDL 7.1, with support for some IDL 8.0 features (for more information see
https://github.com/gnudatalanguage/gdl).
Both the source code and precompiled executables for various platforms are available.
When used to run IDL-Healpix routines, GDL 1.0.1 or more gives
very satisfactory results6.
The calculations agree with those done under IDL, with
comparable computation times, but a few minor features, mostly related to the font selection, are missing.
To fully enjoy GDL capabilities
- HEALPix 3.83 or more must be installed
- Besides the mandatory requirements (plplot,
gsl,
readline
and
zlib)
GDL must also have been (pre-)compiled with links to
- ImageMagick
(or GraphicsMagick)
to produce GIF, JPEG and PNG output files, and
- pslib
(recommended, but not required)
to produce PostScript and PDF files (in the latter case,
a recent version of ghostscript, i.e. 9.07 or more, is also recommended).
- When run under GDL 1.0.1, and if the requirements stated above are met,
the visualization routines
azeqview, cartview, gnomview, mollview and orthview
will produce correct screen (X) outputs and PS, PDF, PNG, GIF, and JPEG images, with the following caveat(s):
- the pfonts keyword will not allow the selection of other fonts than Hershey vectorial fonts (pfonts[0]=-1).
All other features work properly, including the Latex keyword.
Using FL instead of IDL
Fawlty Language (FL) is a black-box implementation of IDL 8.0, for which precompiled self-contained packages
are available for Linux, Windows, MacOSX and more from
https://www.flxpert.hu/fl.
Most of the IDL routines and features have been implemented, with a few exceptions
(like xloadct) and the restrictions listed below.
To fully enjoy FL capabilities
- HEALPix 3.83 or more must be installed,
- the version 0.79.50 or more of FL must be used,
- it is recommended to set the environment variable FL_DIR to the FL top directory (ie path/fl/fl_0.79.50 in Linux and Windows, and path/fl.app in MacOSX)
in order for the HEALPix enabled FL tools (hfl and hflde) to be defined properly during the
IDL/GDL/FL configuration.
- to produce PDF files
a recent version of ghostscript, i.e. 9.07 or more, is recommended.
- In FL, the !p.font selection is ignored in the 'X' device.
In 'PS' device, the Hershey Fonts (!p.font=-1) and Device Fonts (!p.font=0)
look respectively slightly and noticeably different from their IDL counterparts,
while the TrueType Fonts (!p.font=1) are not fully implemented yet.
As a consequence, the graphical outputs of
azeqview, cartview, gnomview, mollview and orthview
will look slightly different in FL and IDL,
while in those routines the option
PFONTS will not work fully as expected.
However, the Latex keyword will work properly in those routines.
Appendix I: Recent Changes and New Features
- Support for intel ifx compiler
- Proper detection of python versions 3.10 and above
- configuration, compilation and installation of healpy package via pip.
- Switch to
healpy 1.18.0
(CHANGELOG)
- now supports python
- scipy and matplotlib are now optional dependencies
- wheels available for MacOS arm64
- addition of resize_alm
- bugs correction in query_disc and query_polygon
- ships with cfitsio 4.5.0
- Corrected documentation of pix2vec routines
- Cfitsio 4.1.0 (March 2022) and higher now properly supported
- Bug corrections in
input_map and
read_fits_partial,
- added a workaround for a bug detected in Apple-ARM-chips implementation of gfortran 11.
- Note that cfitsio 4.1.0 or higher is required for Fortran codes running on Apple's ARM chips
- Switch to
healpy 1.16.1
(CHANGELOG)
- Updated CFITSIO included in healpy to 4.1.0, necessary for compatibility with Apple ARM chips
- Update HEALPix C++ sources to revision 1206 (just maintenance commits)
- Do not normalize binary arrays
- Fix unncessary log warning message in plots
- Fixed double application of margins in visualization functions when using subplot syntax and implemented margins parameter for mollview, orthview, and azeqview when subplot syntax is not used
- Fixed reuse_axes=True for cartview and gnomview
- New features in projview: subplots, remove monopole-dipole, labels, tickmarks, graticule, Planck and WMAP colormaps
- Fixed the CFITSIO version mismatch warning
- Added colorbar ticks and normalization
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.81
- Cfitsio 4.0.0 (Jul 2021) and higher now properly supported
- Introduced workarounds for some minor GDL and FL limitations.
- Switch to
healpy 1.15.2
(CHANGELOG)
- new function blm_gauss to generate alm of a gaussian beam,
- implement rotation in the graticule of projview,
- explain how to create a local datapath for pixel weights,
- improvement on is_seq to avoid synalm breaking on JAX input arrays, added unit tests,
- upgraded HEALPix C++ sources to HEALPix 3.81, fixing incompatibility with CFITSIO 4
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.80
- addition of
SHARP_PARAL and
CXX_PARAL
to control the parallel implementation of the libsharp library and C++ library and codes;
- PYTHON now defaults to python3
- the line-integral convolution interface is now accessible not only from the command line, but also via C++ calls, to allow calling from healpy;
- some internals were restructured to allow easier integration with SWIG
- Improvement of query_disc routine in inclusive mode,
- the routines
alm2map_spin and
map2alm_spin now accept any (integer) spin values
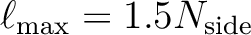 , but the scalar routines
alm2map and
map2alm are still recommended for vanishing spin (s=0),
, but the scalar routines
alm2map and
map2alm are still recommended for vanishing spin (s=0),
- correction of bugs preventing the compilation with versions 10.* of gfortran,
- fixed bug affecting map2gif when compiled with versions 10.* of gfortran and gcc.
- Switch to
healpy 1.15.0
(CHANGELOG)
- write_map keeps dtype of input map array instead of float32; read_map keeps dtype of FITS file instead of upcasting to float64; write_cl uses dtype of input cl instead of float64
- Changed all warnings to using the logging module, deprecated all verbose keywords
- Flip sign for spin-0 alm2map_spin and map2alm_spin; fixed map2alm_spin bug for masked input
- Support transparency in plotting with the alpha parameter
- Experimental projview function to plot maps using projections from matplotlib
- Removed the note that we will change order of cl in synfast and synalm, we will leave new=False default
- Added convenience functions order2npix and npix2order
- Support nested maps hp.smoothing; fixed indexing issue in bl2beam
- Allow OBJECT FITS header not to be a string
- Drop support for Python 2.7-3.5; Improvements of the build system; Automatically build wheels for Linux/MacOS on Github actions
- and other minor bug fixes ...
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.70 (2020-07)General
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
IDL
Python
- Switch to
healpy 1.14.0
(CHANGELOG)
- Line Integral Convolution plots to plot polarization,
- fixed FITS files that were left open,
- increased precision in coordinate transforms,
- fix propagation on mmax in smoothing,
- reworked verbose,
- and many other improvements and bugs fixes ...
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.60 (2019-12)General
- The computation time of a map synthesis or analysis has been reduced
(for instance, by at least 30% at
Nside=2048 and
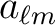 ),
with the same memory footprint and numerical accuracy as previously, thanks to
),
with the same memory footprint and numerical accuracy as previously, thanks to
- major performance increase for Spherical Harmonics Transforms
in the libsharp C-written library
called by the C++, F90, IDL and python routines and facilities,
thanks to ideas of Keiichi Ishioka
(https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2018-019
and personal communication);
- the possibility of building the libsharp library with simultaneous support for different x86 CPU
features (SSE2, AVX, AVX2, FMA3, FMA4, AVX512F); the appropriate set of
subroutines being selected automatically at runtime.
- The configure script will ensure
a single and seamless configuration, compilation and installation
of the libsharp library,
even if several language implementations of HEALPix are compiled.
- The configure script now supports
an automated mode beside the usual interactive mode, and some environment variables
can be used to customize its behavior in both modes
(eg, choice of compilers and their options).
C++
- Link to the new and faster libsharp library
- Simpler configuration with the systematic use of autotools
- The C++ binaries, libraries and header files now installed in
${HEALPIX}/bin,
${HEALPIX}/lib and
${HEALPIX}/include directories respectively.
- Added documentation for the module needlet_tool.
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
- Link to the new and faster libsharp library
- Some external C routines replaced by Fortran 2003 extensions.
IDL
- Faster isynfast, ianafast, ismoothing routines
- addition of outline_earth to create a structure outlining Earth features such as coastlines, rivers, country boundaries, ...
- azeqview, cartview, gnomview, mollview,
orthview visualization routines: support for color and thickness in outline keyword
- Update of the required
IDL-astron library
routines, and Coyote
library
routines (2019-10-30).
Python
- Switch to
healpy 1.13.0
(CHANGELOG)
- different handling of default dtype in read_cl, write_cl and read_map
- implemented dist2holes, distance from pixel center to closest invalid pixel
- allow not-power-of-2
Nside for RING
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.50 (2018-11)
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
C++
IDL
Python
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.40 (2018-06)
General
- A new set of (pixel-based) quadrature weights has been introduced, besides the older ring-based ones, to improve the accuracy of the Spherical Harmonics calculation. For maps
containing a signal that is band-limited at
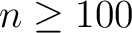 , this allows
recovery of the
, this allows
recovery of the 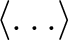 at almost machine precision. They are supported by map-analysis routines in C++, Fortran, IDL and Python.
The weights for power-of-2 values of
Nside in
at almost machine precision. They are supported by map-analysis routines in C++, Fortran, IDL and Python.
The weights for power-of-2 values of
Nside in
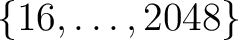 are precomputed and shipped in
Healpix/data/weight_pixel_n?????.fits,
and the missing ones can be computed for any value of
Nside with the compute_weights C++ facility.
are precomputed and shipped in
Healpix/data/weight_pixel_n?????.fits,
and the missing ones can be computed for any value of
Nside with the compute_weights C++ facility.
C++
- IMPORTANT: the syntax for specifying ring weights and pixel windows has
changed! This affects the facilities anafast_cxx, smoothing_cxx,
udgrade_harmonic_cxx, alm2map_cxx, mult_alm_cxx.
Pixel window files have to be specified (with path) using the parameter
windowfile; ringweights is used for ring weight files, and pixelweights
for pixel weight files.
- Full pixel quadrature weights are now supported in map analysis facilities such as anafast_cxx, smoothing_cxx and udgrade_harmonic_cxx
using the pixelweights parameter.
- Experimental needlet_tool code for needlet analysis
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
- The facilities
anafast and
smoothing now support pixel-based quadrature weights.
Introduction of the supporting
nside2npweights,
unfold_weightsfile,
get_healpix_weight_file,
get_healpix_pixel_weight_file.
- The subroutine
input_map in its default mode
and the facilities
anafast,
median_filter,
smoothing, and
ud_grade
test the value of the POLCCONV FITS keyword when reading a polarized map,
and interpret the polarization accordingly,
as described in the note on POLCCONV in The HEALPix Primer.
- median_filter facility and
median subroutine: faster by moving an internal array from heap to stack; do not crash anymore when dealing with empty data sets;
slightly different output of median_filter: when median is computed over an even number of pixels
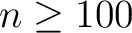 , sorted in [1,n],
the output is d(n/2) instead of
(d(n/2)+d(n/2+1))/2 previously. Result remains d(n/2+1) for odd n.
, sorted in [1,n],
the output is d(n/2) instead of
(d(n/2)+d(n/2+1))/2 previously. Result remains d(n/2+1) for odd n.
IDL
Python
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.31 (2016-08)
General
- Detailed HOWTO for installation under Windows;
- Interactive configure script now supports MINGW environment (for Windows),
and better detects gcc and python versions;
- Improved cross-document linking in PDF documentation.
C++
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
IDL
Python
- Switch to
healpy 1.9.1
(CHANGELOG)
- Removed C++ 11 features
- Streamlined setup.py
- Plotting fixes for Python 3
- Numpy 1.10 fix
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.30 (2015-10)
C++
- support for multi-order coverages (MOC);
- allow generation of
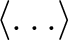 from 6-component power spectra;
from 6-component power spectra;
- moved from alice2 to alice3, which produces FITS HEALPix maps as output.
These can be visualized more flexibly with external tools.
- switch from custom xcomplex class to std::complex;
- rangeset class has been redesigned.
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
- anafast facility now produces nine spectra
(TT, EE, BB, TE, TB, EB, ET, BT and BE), instead of six previously,
when analyzing two polarized maps;
- alm2cl subroutine can now produces nine spectra
(TT, EE, BB, TE, TB, EB, ET, BT and BE), instead of six previously, when
called with two sets of polarized
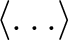 and can also symmetrize
the output
and can also symmetrize
the output 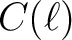 if requested;
if requested;
- the
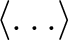 generated by
create_alm subroutine can now take into account
non-zero (exotic) TB and EB cross-spectra (option polar=2) if the input FITS file contains the relevant information
generated by
create_alm subroutine can now take into account
non-zero (exotic) TB and EB cross-spectra (option polar=2) if the input FITS file contains the relevant information
- new routines nest2uniq
and uniq2nest for conversion
of standard pixel index to/from Unique ID number. See "The Unique Identifier scheme" section in "HEALPix Introduction Document"
for more details.
- improved
repeat
behavior in write_bintabh routine
- edited map2alm_iterative
routine to avoid a bug specific to Intel's Ifort 15.0.2
- CFITSIO version 3.20 (August 2009) or more now required;
IDL
- azeqview, cartview, gnomview, mollview, orthview
visualization routines:
- addition of PDF keyword for production of Adobe PDF outputs;
- addition of LATEX keyword for genuine
or emulated LATEX processing of character strings;
- addition of PFONTS keyword to select
origin and type of character font;
- the CROP keyword now has the same behavior for all output media (GIF, JPEG, PDF, PNG, PS, ... and X); the NOBAR keyword now removes the color bar or the polarization color wheel, as applicable; correct EQUINOX date in header of output FITS map; the double precision maps and those with constant value are now correctly handled.
- fits2cl: addition of /PLANCK2 keyword
to read best fit
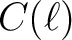 model to Planck 2015 data.
model to Planck 2015 data.
- new routines nest2uniq and uniq2nest for conversion of standard pixel index to/from Unique ID number. See "The Unique Identifier scheme" section in "HEALPix Introduction Document"
for more details.
- HEALPix enabled GDL commands (hgdl and hgdlde) are defined during the
configuration process.
- update of the required
IDL-astron library
routines, and Coyote
library
routines (2015-09-23).
Java
- deprecated parts of the library have been removed;
- MOC support (see
http://ivoa.net/documents/MOC/
for high-level description);
- queries for arbitrary polygons (using MOC);
- new targets in build.xml which allow compilation without external JARs.
Python
- switch to healpy
1.9.0
- same C++ source code as HEALPix 3.30
- drop support for Python 2.6
- support for astropy.fits
- improvements to read_map and write_map
- renamed get_neighbours to get_interp_weights
- several bug fixes in build and installation processes
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.20 (2014-12)
General
C
- Top configure script now proposes compilation with or without
CFITSIO-related functions
- Improved autotools support
C++
- automatic workaround for bugs in older versions of GNU g++ compiler
(bug reports
37,
45,
48,
51)
- workaround for possible bug in Intel icc 14.0 compiler
- bug fix in Mollweide projection in map2tga when not looking at (0,0)
- autotools updates
- deprecation warnings in alice2, soon to be replaced
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
IDL
Java
- explicit deprecation warnings in the source codes
Python
- switch to healpy
1.8.1
- fixes bugs in monopole removal,
- adds orthographic projection,
- easier install on MacOSX
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.11 (2013-04)
General
- libsharp
C library used for Spherical Harmonics Transforms
in Fortran and C++ since HEALPix 3.10
can now be compiled with any gcc version.
C++
- See General section above
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
- bug correction in query_disc
routine in inclusive mode
- bug correction in alm2map_spin
routine, which had its spin value set to 2
- See General section above
IDL
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.10 (2013-03)
General
N/AC
- experimental GNU autotools support (undocumented); the standard
configuration script remains available
C++
- Spherical Harmonics Transform library libpsht replaced by libsharp
(Reinecke & Seljebotn, 2013).
Note that
some gcc versions
(4.4.1 to 4.4.6) crash with an internal compiler error during compilation of libsharp.
The problem has been fixed in gcc 4.4.7, 4.5.*, 4.6.*, 4.7.* and
newer versions and was not present in versions 4.2.* and 4.3.*.
- added boundaries() method to T_Healpix_Base
- experimental GNU autotools support (undocumented); the standard
configuration script remains available
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
- all Fortran facilities now support most of cfitsio's "Extended File
Name Syntax" features,
allowing the reading and processing of an arbitrary HDU and table column out of
remote, compressed FITS files. For example, setting
infile = ftp://url/file.fits.gz[extn][col colname]
in anafast
will download the FITS file file.fits.gz from url,
uncompress it, open the HDU (extension) featuring keyword EXTNAME=extn, or the one with 1-based rank number extn, read the table column
with TTYPE*=colname out of it and will analyze it.
It is also possible to perform a remote anafast analysis of a
Planck Legacy Archive (PLA)
sky map named map.fits via the PLA AIO
Subsystem
by simply setting
infile=https://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?MAP.MAP_ID=map.fits
as input map file.
- yet faster
synfast,
anafast,
smoothing thanks to libsharp
routines (see warning on
gcc releases above).
IDL
Java
N/APython
- switch to healpy 1.5.0: addition of
gauss_beam
to generate Gaussian beam window function.
Bug corrections and Improvements in Version 3.0 (2012-11)
General
Introduction of the script healpix_doc for easy access to the HEALPix
PDF and HTML documentation.
C
- Interface has remained unchanged, but the code has been replaced by a C port
of the relevant Healpix C++ functions, resulting in significant speedups.
- Additional functions are provided which support Nside values up to 229.
They have the same name as the traditional functions, with a "64" suffix appended.
C++
- Query routines:
query_polygon() and query_polygon_inclusive() added.
Query routines now return lists of pixel ranges instead of lists of pixels,
which is much more economic.
Inclusive query routines: tradeoff between performance and number of false
positives is tuneable.
Queries now work natively in both NESTED and RING schemes. Operations on
the NESTED scheme are typically slower than in RING, but still much faster
than computing the query in RING and converting all pixel numbers to NESTED
afterwards.
- Healpix_Base:
Healpix_Base and Healpix_Base2 have been merged into the templated class
T_Healpix_Base; functionality is still available under the old names.
Various performance improvements to T_Healpix_Base functionality
- User-friendliness:
module parameters can now optionally be passed on the command line instead
of using a parameter file. For example:
anafast_cxx nlmax=500 infile=test.fits iter_order=3
Facilities now check input maps for undefined pixels before calling map2alm().
If undefined pixels are found, a warning is printed, and the pixels are set
to zero. udgrade_cxx refuses downgrading of polarised maps (which would produce
unphysical results)
- Bug fixes: accuracy of pix2ang near the poles at high resolutions has been improved.
- Configuration: optional autoconf support
- Interface changes:
- Healpix_Base::query_*(): new interface
- cxxutils.h has been split up into
announce.h (dealing with module banners),
share_utils.h (dealing with subdividing tasks between multiple workers) and
string_utils.h (dealing with string manipulation and file parsing)
- psht.h: interface to alm_info changed in order to add MPI support
- ylmgen_c.h: Ylmgen_init() interface has changed
- bluestein.h: bluestein_i() interface changed
Fortran 90 facilities
and
subroutines
- Compressed and/or remote (ftp or http) FITS files can now be
read. CFITSIO 3.14 or more is now required;
- introduction of the
process_mask
facility to compute the angular distance of valid
pixels to the closest invalid pixels for a input binary mask, and of the
supporting routines
dist2holes_nest,
fill_holes_nest,
maskborder_nest,
size_holes_nest;
- the pixel query routine
query_disc
has been improved and will return fewer
false positive pixels in the
inclusive mode;
- improved accuracy of the co-latitude calculation in the vicinity
of the poles at high resolution in
nest2ring, ring2nest, pix2ang_*, pix2vec_*,
 ;
;
- sky_ng_sim now allows the computation
of the spatial derivatives of the non Gaussian map being produced, and the
output of the
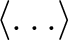 coefficients of that map;
coefficients of that map;
- anafast now allows the
pro/down-grading of the input mask to match the resolution of the map(s) being
analyzed;
- the median filter routine medfiltmap, used by the facility
median_filter is now parallelized.
IDL
- New routines to go from circular beam profile to transfer function
(beam2bl),
and back (bl2beam);
to go from indexed list of
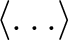 to a(l,m) 2D table
(alm_i2t),
and back
(alm_t2i); and to compute the angular distance
between pairs of vectors (angulardistance).
to a(l,m) 2D table
(alm_i2t),
and back
(alm_t2i); and to compute the angular distance
between pairs of vectors (angulardistance).
- addition of iprocess_mask
interface to F90 process_mask facility to compute the angular distance of valid
pixels to the closest invalid pixels for a input binary mask.
- creation of hpx2dm routine to generate
DomeMaster images of HEALPix maps that can be projected on planetariums.
- the pixel query routines
query_triangle,
query_polygon,
and in particular query_disc,
have been improved and will return fewer
false positive pixels in the inclusive mode
- improved accuracy of the co-latitude calculation in the vicinity
of the poles at high resolution in
nest2ring, ring2nest, pix2ang_*, pix2vec_*,
- cartview, gnomview, mollview, orthview:
the length and spacing of the headless vectors used to represent
polarization is now user-controlled via
POLARIZATION
keyword. The COLT keyword now
allows the use of an interactively modified color table.
- orthview now accepts
STAGGER keyword to overplot staggered
spheres (with a twist) in order to detect periodic boundary conditions on the
sky
- fits2cl: addition of WMAP7 keyword
to read best fit C(l) model to WMAP 7yr data.
- read_fits_map can now read
Nside=8192 HEALPix maps and is generally faster than previously for smaller
maps
- update of astron library routines (01-Feb-2012).
Java
- Core functionality has been reimplemented from scratch in the form of the
"healpix.essentials" package. It is strongly recommended to use this package
directly in future projects making use of Java HEALPix.
"healpix.essentials" is a port of the Healpix C++ library and presents a very
similar interface.
The "healpix.core" package is still provided. It uses "healpix.essentials"
internally, and its interface has been kept stable as much as possible.
Some adaptations in user code will still be necessary, however.
Please note that using "healpix.core" will result in slightly lower performance
than calling "healpix.essentials" methods directly, because of the necessary
data conversion.
- New features and improvements introduced with the HealpixBase class, compared
to the HealpixIndex, Healpix and PixTools classes:
- close similarities with Healpix_Base_T class from Healpix C++, which allows
simultaneous development and bug fixes for both.
- support for arbitrary positive Nside values in RING scheme; no longer limited
to powers of 2
- maximum supported Nside value: 229
- significant performance improvements: most methods have been accelerated
by integral factors, some by more than an order of magnitude.
- re-implementation of queryDisc and queryPolygon, with same new features
as the C++ implementation (see above).
- the HealpixProc class offers a procedural (instead of object-oriented)
interface to the HealpixBase functionality, which simplifies transition
for users of the "Healpix" and "PixTools" classes.
NOTE: this only works for Nside parameters which are powers of 2
- many bug fixes
- no external library dependencies, except for "nom.tam.fits" if FITS I/O is
required
Python
- the
healpy
package (C. Rosset, A. Zonca et al.) is now part of HEALPix
HEALPix Facility Installation Guidelines
This document was generated using the
LaTeX2HTML translator Version 2020 (Released January 1, 2020)
The command line arguments were:
latex2html -dir ../../healpix-dynamicPages/html -up_url main.htm -up_title 'Main Page' -down_url main.htm -down_title 'Main Page' -math -html_version 5.0,latin1 -antialias -bottom_navigation -short_extn -white -local_icons -noexternal_images -address 'Version 3.83, 2024-11-13' -info 1 -toc_depth 8 -split 3 -prefix install -external_file ./install -t 'Installing HEALPix' install
The translation was initiated on 2024-11-13
Version 3.83, 2024-11-13
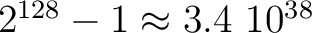 .
.
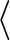 OS_TYPE
OS_TYPE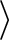 /config
or in
/config
or in
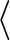 OS_TYPE
OS_TYPE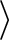 /config
if ./configure -L was used)
according to shell
type in which various environment variables and aliases are defined
for your convenience. If you agree upon prompting
(or set the boolean
environment variable PROFILE_EDIT to an affirmative value),
it will also change your default system profile during installation to
automatically source this profile. If you do not agree to this change
(or set the boolean environment variable PROFILE_EDIT to a false value),
you will need to explicitly source the configuration file above for any session in
which you intend to run HEALPix facilities.
In particular, you will have to make sure that the HEALPIX system variable is correctly
defined (as the full path to the HEALPix directory) before running
the package.
/config
if ./configure -L was used)
according to shell
type in which various environment variables and aliases are defined
for your convenience. If you agree upon prompting
(or set the boolean
environment variable PROFILE_EDIT to an affirmative value),
it will also change your default system profile during installation to
automatically source this profile. If you do not agree to this change
(or set the boolean environment variable PROFILE_EDIT to a false value),
you will need to explicitly source the configuration file above for any session in
which you intend to run HEALPix facilities.
In particular, you will have to make sure that the HEALPIX system variable is correctly
defined (as the full path to the HEALPix directory) before running
the package.
 you want to use to visualize the
GIF, JPEG, PDF, Postscript and PNG files created by IDL, GDL or FL.
you want to use to visualize the
GIF, JPEG, PDF, Postscript and PNG files created by IDL, GDL or FL.
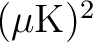 , and is therefore different from the one
included in releases 1.* (that can still be found in cl_old.fits).
, and is therefore different from the one
included in releases 1.* (that can still be found in cl_old.fits).
 , all in
, all in
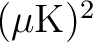 and defined on the multipole range
and defined on the multipole range
![$[0, \ell_{\mathrm{max}}]$](installimg7.png) , have been included for convenience in
Healpix_3.83/test/
in a HEALPix compatible format.
, have been included for convenience in
Healpix_3.83/test/
in a HEALPix compatible format.
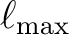
 ) type:
) type:
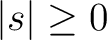 2.7.*, or
2.7.*, or
 2.8.*
2.8.*
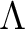
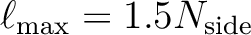 , but the scalar routines
alm2map and
map2alm are still recommended for vanishing spin (s=0),
, but the scalar routines
alm2map and
map2alm are still recommended for vanishing spin (s=0),
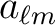 ),
with the same memory footprint and numerical accuracy as previously, thanks to
),
with the same memory footprint and numerical accuracy as previously, thanks to
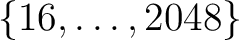 -CDM
-CDM 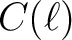 model which best fits the 2018 Planck data analysis (available from Healpix/test/planck2018_lcdm_cl_v3.fits);
model which best fits the 2018 Planck data analysis (available from Healpix/test/planck2018_lcdm_cl_v3.fits);
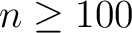 , this allows
recovery of the
, this allows
recovery of the  at almost machine precision. They are supported by map-analysis routines in C++, Fortran, IDL and Python.
The weights for power-of-2 values of
Nside in
at almost machine precision. They are supported by map-analysis routines in C++, Fortran, IDL and Python.
The weights for power-of-2 values of
Nside in
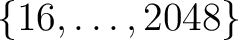 are precomputed and shipped in
Healpix/data/weight_pixel_n?????.fits,
and the missing ones can be computed for any value of
Nside with the compute_weights C++ facility.
are precomputed and shipped in
Healpix/data/weight_pixel_n?????.fits,
and the missing ones can be computed for any value of
Nside with the compute_weights C++ facility.
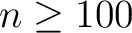 , sorted in [1,n],
the output is d(n/2) instead of
(d(n/2)+d(n/2+1))/2 previously. Result remains d(n/2+1) for odd n.
, sorted in [1,n],
the output is d(n/2) instead of
(d(n/2)+d(n/2+1))/2 previously. Result remains d(n/2+1) for odd n.
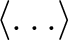 from 6-component power spectra;
from 6-component power spectra;
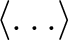 and can also symmetrize
the output
and can also symmetrize
the output 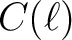 if requested;
if requested;
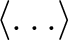 generated by
create_alm subroutine can now take into account
non-zero (exotic) TB and EB cross-spectra (option polar=2) if the input FITS file contains the relevant information
generated by
create_alm subroutine can now take into account
non-zero (exotic) TB and EB cross-spectra (option polar=2) if the input FITS file contains the relevant information
 model to Planck 2015 data.
model to Planck 2015 data.
 ).
).
 ;
;
 coefficients of that map;
coefficients of that map;
 to a(l,m) 2D table
(alm_i2t),
and back
(alm_t2i); and to compute the angular distance
between pairs of vectors (angulardistance).
to a(l,m) 2D table
(alm_i2t),
and back
(alm_t2i); and to compute the angular distance
between pairs of vectors (angulardistance).