alm2map_spin*
This routine produces the maps of arbitrary spin 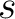 and
and 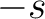 given their alm
coefficients.
A (complex) map
given their alm
coefficients.
A (complex) map 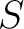 of spin
of spin 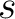 is a linear combination of the spin weighted harmonics
is a linear combination of the spin weighted harmonics
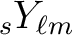
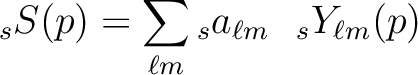 |
(3) |
for
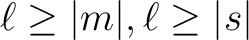 ,
and is such that
,
and is such that
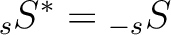 .
.
The
usual phase convention for the spin weighted harmonics
is
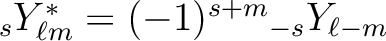 and therefore
and therefore
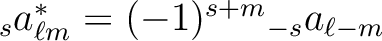 .
.
alm2map_spin* expects the alm coefficients to be provided as
for 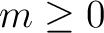 , knowing that, just as for spin 0 maps, the
coefficients for
, knowing that, just as for spin 0 maps, the
coefficients for 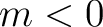 are given by
The two (real) maps produced by alm2map_spin* are defined respectively as
With these definitions,
are given by
The two (real) maps produced by alm2map_spin* are defined respectively as
With these definitions, 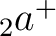 ,
, 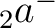 ,
, 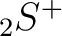 and
and 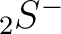 match HEALPix polarization
match HEALPix polarization
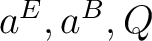 and
and  respectively. However, for
respectively. However, for
 ,
,
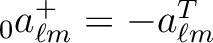 ,
,
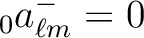 ,
,
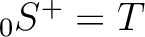 ,
,
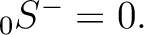
When dealing only with scalar quantities, like temperature or intensity maps, having a spin 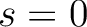 , it is
highly recommended, and much more memory-efficient, to use directly the routine alm2map, rather then setting spin
, it is
highly recommended, and much more memory-efficient, to use directly the routine alm2map, rather then setting spin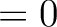 in alm2map_spin*.
Location in HEALPix directory tree: src/f90/mod/alm_tools.F90
in alm2map_spin*.
Location in HEALPix directory tree: src/f90/mod/alm_tools.F90
FORMAT
ARGUMENTS
| name & dimensionality |
kind |
in/out |
description |
|---|
| |
|
|
|
|
nsmax |
I4B |
IN |
the
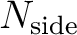 value of the map to synthesize. value of the map to synthesize. |
| nlmax |
I4B |
IN |
the maximum 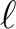 value used for the value used for the
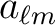 . . |
| nmmax |
I4B |
IN |
the maximum 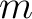 value used for the value used for the
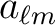 . . |
| spin |
I4B |
IN |
spin 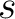 of the maps to be generated (only its absolute value
is relevant). of the maps to be generated (only its absolute value
is relevant). |
| alm(1:2, 0:nlmax, 0:nmmax) |
SPC/ DPC |
IN |
The
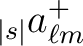 and and
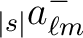 values to make the map
from. values to make the map
from. |
| map(0:12*nsmax**2-1, 1:2) |
SP/ DP |
OUT |
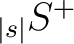 and and
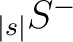 output maps output maps |
| zbounds(1:2), OPTIONAL |
DP |
IN |
section of the sphere on which to perform the map synthesis, expressed in terms of
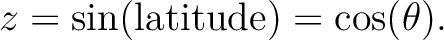 If zbounds(1) If zbounds(1)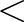 zbounds(2), it is
performed on the strip zbounds(1) zbounds(2), it is
performed on the strip zbounds(1)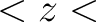 zbounds(2); if not,
it is performed outside the strip
zbounds(2) zbounds(2); if not,
it is performed outside the strip
zbounds(2)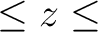 zbounds(1). If absent, the whole map is processed. zbounds(1). If absent, the whole map is processed.
|
EXAMPLE:
use healpix_types
use pix_tools, only : nside2npix
use alm_tools, only : alm2map_spin
integer(I4B) :: nside, lmax, mmax, npix, spin
real(SP), dimension(:,:), allocatable :: map
complex(SPC), dimension(:,:,:), allocatable :: alm
...
nside=256 ; lmax=512 ; mmax=lmax ; spin=4
npix=nside2npix(nside)
allocate(alm(1:2,0:lmax,0:mmax))
allocate(map(0:npix-1,1:2))
...
call alm2map_spin(nside, lmax, mmax, spin, alm, map)
Make spin-4 maps from the
 passed in alm. The maps have
passed in alm. The maps have
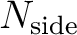 of 256, and are constructed from
of 256, and are constructed from
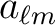 values up to 512 in
values up to 512 in 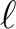 and
and 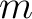 .
.
MODULES & ROUTINES
This section lists the modules and routines used by alm2map_spin*.
-
ring_synthesis
- Performs FFT over
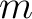 for synthesis of the rings.
for synthesis of the rings.
-
compute_lam_mm, get_pixel_layout,
-
gen_lamfac_der, gen_mfac, gen_mfac_spin, do_lam_lm_spin,
-
gen_recfac, gen_recfac_spin, init_rescale, l_min_ylm
- Ancillary routines used
for
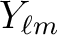 recursion
recursion
-
misc_utils
- module, containing:
-
assert_alloc
- routine to print error message, when an array can not be
allocated properly
Note: Starting with version 3.80, some libsharp routines will be called for any  value.
value.
RELATED ROUTINES
This section lists the routines related to alm2map_spin*
-
alm2map
- routine generating maps of temperature
and polarisation from their
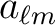
-
alm2map_der
- routine generating maps of temperature
and polarisation, and their spatial derivatives, from their
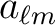
-
map2alm_spin
- routine performing the inverse transform
of alm2map.
-
create_alm
- routine to generate randomly
distributed
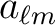 coefficients according to a given power spectrum
coefficients according to a given power spectrum
Version 3.83, 2024-11-13
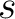 and
and 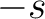 given their alm
coefficients.
A (complex) map
given their alm
coefficients.
A (complex) map 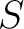 of spin
of spin 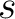 is a linear combination of the spin weighted harmonics
is a linear combination of the spin weighted harmonics
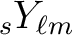
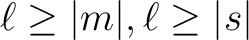 ,
and is such that
,
and is such that
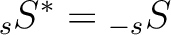 .
.
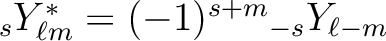 and therefore
and therefore
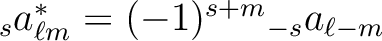 .
.
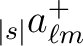
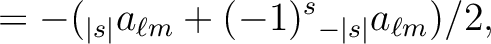
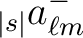
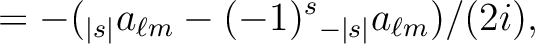
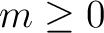 , knowing that, just as for spin 0 maps, the
coefficients for
, knowing that, just as for spin 0 maps, the
coefficients for 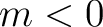 are given by
are given by
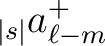
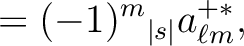
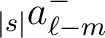
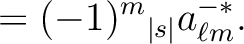
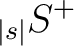
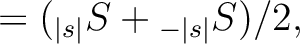
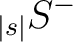
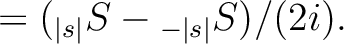
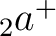 ,
, 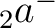 ,
, 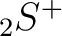 and
and 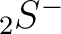 match HEALPix polarization
match HEALPix polarization
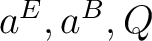 and
and 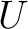 respectively. However, for
respectively. However, for
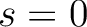 ,
,
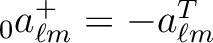 ,
,
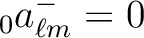 ,
,
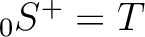 ,
,
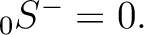
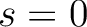 , it is
highly recommended, and much more memory-efficient, to use directly the routine alm2map, rather then setting spin
, it is
highly recommended, and much more memory-efficient, to use directly the routine alm2map, rather then setting spin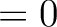 in alm2map_spin*.
Location in HEALPix directory tree: src/f90/mod/alm_tools.F90
in alm2map_spin*.
Location in HEALPix directory tree: src/f90/mod/alm_tools.F90
passed in alm. The maps have
of 256, and are constructed from
values up to 512 in
and
.
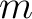 for synthesis of the rings.
for synthesis of the rings.
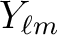 recursion
recursion
 value.
value.
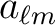
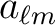
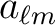 coefficients according to a given power spectrum
coefficients according to a given power spectrum