Previous: ring_synthesis Up: HEALPix Fortran90 Subroutines Overview Next: same_shape_pixels_nest, same_shape_pixels_ring Top: Main Page
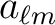 coefficients to
emulate the effect of an arbitrary rotation of the underlying map. The rotation is done
directly on the
coefficients to
emulate the effect of an arbitrary rotation of the underlying map. The rotation is done
directly on the
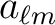 using the Wigner rotation matrices, computed by
recursion.
To rotate the
using the Wigner rotation matrices, computed by
recursion.
To rotate the
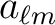 for
for
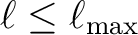 the number of
operations scales like
the number of
operations scales like
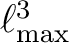 .
.
call rotate_alm*( nlmax, alm_TGC, psi, theta, phi )
| name & dimensionality | kind | in/out | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nlmax | I4B | IN | maximum 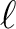 value for the value for the
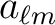 . . |
| alm_TGC(1:p,0:nlmax,0:nlmax) | SPC/ DPC | INOUT | complex
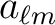 values
before and after rotation of the coordinate system.
The first index here runs from 1:1 for
temperature only, and 1:3 for polarisation. In the latter
case, 1=T, 2=E, 3=B. values
before and after rotation of the coordinate system.
The first index here runs from 1:1 for
temperature only, and 1:3 for polarisation. In the latter
case, 1=T, 2=E, 3=B. |
| psi | DP | IN | first rotation: angle 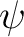 about the z-axis.
All angles are in radians and should lie in [-2 about the z-axis.
All angles are in radians and should lie in [-2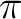 ,2 ,2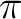 ], the rotations are
active and the referential system is assumed to be right handed, the routine
coordsys2euler_zyz can be used to generate
the Euler angles ], the rotations are
active and the referential system is assumed to be right handed, the routine
coordsys2euler_zyz can be used to generate
the Euler angles
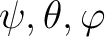 for rotation between standard astronomical coordinate
systems; for rotation between standard astronomical coordinate
systems; |
| theta | DP | IN | second rotation: angle 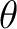 about the original
(unrotated) y-axis; about the original
(unrotated) y-axis; |
| phi | DP | IN | third rotation: angle 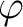 about the original (unrotated) z-axis; about the original (unrotated) z-axis; |
Transforms scalar and tensorfor
to emulate a rotation of the underlying map by (
).
Rotate thefrom Ecliptic to Galactic coordinates.
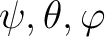 for rotation between standard astronomical coordinate systems
for rotation between standard astronomical coordinate systems
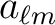 coefficients.
coefficients.
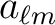 coefficients to apply or remove the effect of an instrumental beam.
coefficients to apply or remove the effect of an instrumental beam.
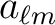 coefficients.
coefficients.
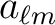 coefficients.
coefficients.
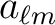 in a FITS file.
in a FITS file.
Version 3.83, 2024-11-13